As per the word “Overtime”, Extra Time can be the meaning of this term. Yes, exactly the same meaning is considered – when employees work more than the standard hours in a day is called overtime.
If someone is working extra, they need to be paid, and that’s why overtime pay for salaried employees is also important. For employees, accurate overtime pay is just as vital. Some good workers in the United States are deprived of overtime they have worked for, which can result in frustration and economic loss.
Determining overtime can become messy when working with various pay rates, fluctuating hours, and federal and state labor regulations. Whether you have a small staff or manage a big workforce, understanding how to calculate and pay overtime improves smooth business operations and creates trust with your employees. In this blog, we will outline overtime pay step by step so that it becomes easier to grasp and implement in real-time.
What Is Overtime Pay?
Overtime is the additional hours an employee puts in over the usual work schedule, and it is associated with extra pay to make up for the added labor.
Overtime in the United States tends to be computed as 1.5 times the employee’s regular hourly wage, a practice often referred to as “time-and-a-half.”
For example;
If a worker’s regular hourly rate is $50, any overtime hours worked outside the regular 40-hour workweek would normally be compensated at $75 per hour. This method guarantees that workers receive fair payment for working extra hours and also incentivizes employers to run workloads effectively.
For companies, utilizing tools such as Check stub generator tools simplifies accurate calculations for overtime and ensures open payroll records, cutting down on conflicts and making employees happy.
Are you struggling to calculate Overtime pay for salaried employees?
Now, don’t worry about net pay, overtime calculations, you can directly do while making the paystubs by using our Paystub Generator Free tool!
Eligibility for Overtime Pay For Salaried Employees
Not all salaried workers are automatically entitled to overtime pay. Eligibility is mostly based on the classification of the employee under U.S. labor laws, specifically the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), and the state’s applicable regulations.
Exempt vs. Non-Exempt Salaried Employees
Salaried workers are categorized as exempt or non-exempt in the USA:
Exempt Employees |
Non-Exempt Salaried Employees |
| These workers are usually executive, administrative, or professional employees who receive a salary that is predetermined by the number of hours worked, regardless of hours worked. Exempt employees are not considered overtime pay for hourly employees. | Salaried employees can also be non-exempt but fail to qualify for exemptions. Non-exempt salaried employees are entitled to overtime compensation, typically computed at 1.5 times the regular hourly pay for work over 40 hours in a workweek. |
Determinants of Overtime Qualifications
A number of determinative factors influence whether a salaried employee qualifies for overtime:
| Salary Level | The FLSA establishes a minimum salary level. Employees who earn less than this level are generally non-exempt and entitled to overtime |
| State Laws | Certain states have more stringent regulations than federal law, which include overtime eligibility for more salaried workers. |
How To Calculate Overtime Pay For Salaried Employees?
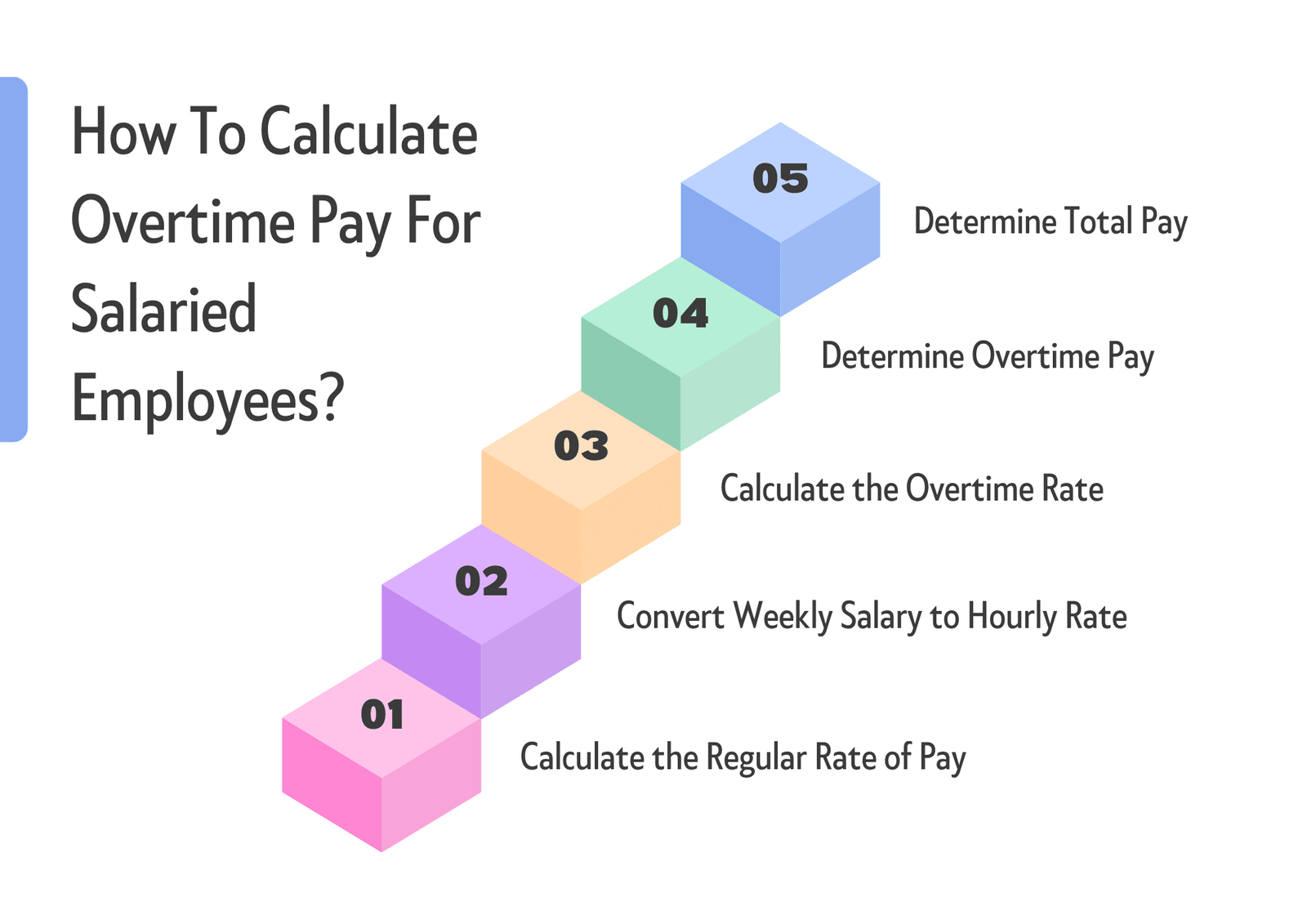
Calculating overtime pay for salaried employees can be more complicated than for hourly employees since salaried employees are usually paid a predetermined amount regardless of the number of hours they work. But breaking the process down into simple steps can lead to a time-and-a-half pay calculation.
-
Step 1: Calculate the Regular Rate of Pay
To begin, if you want to calculate the overtime pay of salaried employees, you start by dividing the worker’s salary by the number of workweeks in a year.
For Example, a worker makes $60,000 a year, and works 50 weeks a year, the worker is paid: $60,000/50 = $1,200 per week
-
Step 2: Convert Weekly Salary to Hourly Rate
Next, you would divide the worker’s weekly pay by the typical number of work hours in a week.
For Example, if the worker works 40 hours a week, then: $1200/40 = $30/hour
-
Step 3: Calculate the Overtime Rate
In general, overtime pay is 1.5 times the hourly rate of pay. Take the hourly rate, and multiply by 1.5
$30 * 1.5 = $45 each hour of overtime
-
Step 4: Determine Overtime Pay
Divide the Overtime rate by the total number of overtime hours worked.
For Example:
A worker working five overtime hours during one week would receive extra pay of $225.00 as overtime pay in addition to regular pay.
-
Step 5: Determine Total Pay
Add up both regular weekly earnings and overtime earnings to determine the total weekly amount earned.
Total Pay: $1200+ $225= $1425.
Read more : What Real Problems Of Paystub Creation Can Be Solved By Paycheck Stub Generator?
Overtime Pay and Taxes
As you calculate overtime pay, keep in mind that tax for overtime pay is levied similarly to regular income. Overtime pay is subject to federal income tax, Social Security tax, Medicare tax, and any state or local taxes due on it.
Example: A salaried employee making $25 an hour in overtime pay receives that amount as an increase to his/her regular pay and is then used for computing withholding tax for overtime payments.
How Overtime Appears In Your Paystub?
When you get your paystub, it spells out precisely how your wages were computed, including overtime pay. Considering the overtime pay for salaried employees is always apparent, but it should be clearly detailed on an accurately prepared paystub.
Here’s what to do:
-
Overtime Hours
Your paystub must reflect the number of hours worked above your regular schedule. Let’s say your regular workweek is 40 hours, and you put in 45 hours. Those additional 5 hours are considered overtime.
-
Overtime Rate
Overtime is generally paid at 1.5 times your regular hourly wage for non-exempt salaried workers. The paystub must reflect this rate, separate from your regular pay.
-
Overtime Earnings
The paystub reflects the amount earned from overtime by multiplying overtime hours worked by the overtime rate.
-
Gross Pay Including Overtime
Your gross total earnings will be your actual salary plus overtime earnings. To have this clearly reflected on a paystub provides visibility and allows you to check your rightful payment.
Summary: Payroll Stub Generator for Accurate Overtime Records
Check stub generator is an effective tool to maintain transparency and accuracy in your payroll, particularly when overtime is payable. Here’s how you can utilize one to your advantage:
- Input Regular Hours and Salary – Enter regular working hours and pay for the pay period. The generator will automatically compute your base pay.
- Add Overtime Hours – Add any additional hours worked in excess of the regular schedule. The generator will apply the proper overtime rate (typically 1.5x) to calculate the extra pay.
- Review Automatic Calculations – A pay stub generator calculates gross, deductions, and net pay, aggregating regular and overtime earnings. When you do the calculation by using a paystub, this minimizes the possibility of human error.
- Create a Professional Paystub – After everything is filled out, the payroll stub generator creates a clean, comprehensive paystub that displays regular pay, overtime pay, deductions, and net pay.
Not only is using a Paystub Generator Free tool time-saving, but it also complies with labor laws by depicting overtime pay for salaried employees accurately. This makes employees and employers both assured that payroll records are accurate.
Read more : Benefits of Using The Paystub Generator Free Tool
FAQs:
-
What is the overtime law for salaried employees in USA?
In the USA, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) governs overtime pay for salaried employees. Non-exempt salaried workers are entitled to 1.5 times their regular pay if their hours worked exceed 40 in any workweek; exempt employees, such as executives, professionals, or administrative roles, typically do not qualify for overtime. Some states may impose stricter labor laws that provide extra protections or requirements.
-
What is the minimum salary to avoid paying overtime?
There is no rule regarding minimum salary, but you can discard non-exempt employees. Simply meeting this amount does not satisfy the exemption criteria; job duties must also meet them; however, certain states, such as California may impose higher minimum salary thresholds to be exempt.
-
How do I calculate my overtime rate?
To calculate an overtime rate, first calculate your regular hourly pay by dividing your weekly salary by the standard number of hours worked per week and multiplying that hourly rate by 1.5 (the standard time-and-a-half rate). For instance, if your weekly salary is $800 and 40 hours are worked each week, the regular hourly pay would be $20; with a time-and-a-half rate added on top, that equals an overtime rate of $30 an hour.
-
How is overtime pay calculated?
Overtime pay for salaried employees is calculated by multiplying an employee’s hourly rate by 1.5 for every hour worked over 40 in one workweek. The weekly salary should be divided by standard work hours to calculate an hourly rate, then multiplied by overtime hours worked, with total gross earnings for that pay period being added together as one figure.
-
What is the maximum number of hours you are allowed to work in one day?
Federal law under the Fair Labor Standards Act does not set an upper limit to how many hours an employee can work per day, instead mandating overtime pay after 40 hours per week are worked.