Whether it’s salary pay or hourly pay, everyone needs perfect clarification on the paycheck stub.
Decisions between salary vs. hourly pay can be among the most crucial for both employers and employees alike. Pay arrangements affect not only earnings, but also work expectations, benefits, overtime eligibility, and long-term job stability. With salaried employees receive fixed pay regardless of hours worked, while hourly employees are typically compensated according to how many hours they work.
Each pay structure affects tax withholding, payroll compliance, employee benefits, scheduling flexibility, and workforce management.
In this guide, we explore hourly to salary employees’ schedules, pay, and many more things. Also, you can learn their related compensation models in detail, while exploring their respective advantages, disadvantages, and real-world implications for businesses and workers alike.
What Is Salary?
Salary pay is a regular form of compensation offered to full-time employees working full-time positions. Employers often distribute salaries on either a biweekly or monthly basis; some organizations may choose alternative payment schedules. Both the amount and frequency are clearly detailed within an employment contract.
Salaried positions typically offer additional perks such as health insurance, paid time off, sick leave and retirement plans – benefits which make salary roles an appealing career option for employees who prioritize stability and long-term career growth.
Salary Meaning
Salary is the fixed sum that employees receive on an ongoing basis from their employer, often quoted as an annual figure and paid biweekly or monthly. With a salary, your paycheck remains constant regardless of how many hours you work each period.
Large employers generally use salary ranges that align with Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) exemption guidelines, along with industry standards, job level requirements, location factors, and market realities. Education levels, prior work experience, performance evaluations, tenure of employment at the company and employee tenure can influence where an employee falls within these salary bands.
Pro Tip: Whether it’s hourly or salary pay, it’s mentioned in your paystub if you use the good Paystub Generator Free tool.
What Is Hourly-Pay? – Hourly-pay Meaning
Hourly-pay refers to an employee being compensated based on the exact number of hours worked instead of receiving a lump-sum paycheck. If employers require additional work from employees, they must compensate them accordingly.
Hourly employees typically qualify for overtime pay. According to US labor law, overtime should typically be compensated at time and a half for hours worked beyond 40 in any workweek; some employers may offer double time pay during holidays or special shifts.
Hourly versus salary employees often earn more, especially if their roles offer frequent overtime. Hourly pay can be attractive in situations with adequate compensation. Hourly pay can help create a healthier work-life balance.
Hourly wages vs salary pay can carry its own risks: during periods of slower business or economic downturns, employers may reduce work hours rather than cut salaried roles.
Common Salaried Jobs in the US
Salaried employment opportunities in the US job market tend to focus on professional and skilled occupations where work is defined by responsibility rather than hourly output. Such roles typically require formal education, specialized training, or experience, and adhere to structured schedules.
Examples of typical salaried jobs in the US include:
- Teacher
- Accountant
- Financial Analyst
- Lawyer
- Software Engineer
These salaried employees’ roles typically attract salary payments since their duties, decisions, and accountability span beyond hourly tracking.
Common Hourly Jobs in the US
Hourly jobs are popular among industries where work hours may fluctuate depending on demand, season, or workload. Employees in hourly roles usually receive payment for all hours worked and sometimes have the opportunity to earn overtime pay during particularly hectic periods.
Hourly jobs that are commonly available in the US:
- Construction Workers
- Servers and Bartenders
- Retail Sales Associates
- Maintenance Technicians
Hourly pay positions provide flexibility and the possibility of earning extra through overtime work, yet may provide less predictable income and benefits compared to salaried roles during slower business periods.
Are you struggling to make a detailed paystub with salary, net pay, and all?
Don’t worry about creating an accurate and professional paystub by using the best payroll stub generator.
Key Facts For Salary Employees
Here are some key facts regarding hourly versus salaried employees that you need to check.
- Professional and Managerial Roles: Salaried pay is most common in administrative, professional, and leadership positions. These roles focus on planning, decision-making, and managing responsibilities rather than tracking hours worked.
- Full-time Commitment: Most salaried positions require a full-time commitment. Employees are expected to complete their duties even if the job occasionally demands longer hours or work outside the typical schedule.
- Fixed Salary: Salaried employees receive a set paycheck at regular intervals, usually monthly or semi-monthly. This amount remains consistent, providing a predictable income regardless of weekly work hours.
- Salary Agreements: Employment contracts clearly define the annual salary, benefits, and job expectations. These agreements help align employer and employee responsibilities from the start.
- Exempt Status: Many salaried roles are classified as exempt under labor laws, which means employees are generally not eligible for overtime pay. This classification is based on job duties and responsibility level.
Key Facts For Hourly Employees
Here are some key facts regarding hourly employees that you need to check.
- Non-exempt Status: Hourly employees typically fall under non-exempt classification under labor law, making them eligible for overtime pay and other wage protections.
- Variable Work Hours: Hourly employees’ schedules can change on a weekly basis, impacting hourly salary either up or down depending on hours worked; overtime pay may apply when standard limits are exceeded.
- Hourly Wage: Employees employed on an hourly basis typically receive a fixed hourly rate; their total compensation depends upon how many hours have been recorded each pay period.
- Part-time Employment Options: Hourly pay is standard in part-time, temporary, and seasonal roles that offer non-fixed schedules for workers looking for flexibility in their schedules.
Pros And Cons of Salary And Hourly Pay
Both salary Vs. hourly Pay structures offer their own set of advantages and disadvantages, depending on your industry, lifestyle needs, and career objectives in the USA. Some individuals might appreciate the security and benefits associated with salaried roles; others may appreciate the flexibility and earnings potential that hourly work provides.
Benefits of Salary Pay
-
Consistent Wage
Salaried employees receive a predetermined income every pay period – even during holidays or sick leave. This salary pay is dependable income that helps with budgeting, relieves financial pressures, and provides stability during unexpected expenses.
-
An Expanding Career Advancement Opportunity
Salaried roles typically come with additional responsibilities and long-term career growth potential, often leading to promotions, leadership roles, and higher earning opportunities.
-
More benefits
Full-time salaried positions often include benefits, including health insurance, paid vacation, and sick leave, as well as employer contributions to retirement plans like 401(k).
Additional perks such as parental leave, wellness benefits, or childcare assistance can provide even more financial security.
Disadvantages of Salary Pay
Salaried employees do not qualify for overtime pay; therefore, employers can require them to work more than 40 hours in a week without offering extra compensation.
Benefits of Hourly Pay
-
Overtime Compensation
Hourly salary is also counted with overtime compensation. During periods of high-volume work, this overtime can significantly boost earnings.
-
Holiday Pay Opportunities
Some employers provide higher pay rates for working holidays, such as double time. Hourly employees in overtime-heavy industries may earn more than salaried workers with similar base pay.
-
Flexibility for other interests
Hourly employment often allows employees to pursue additional educational and skill development programs, side businesses, or jobs outside of work responsibilities once their shift concludes.
Disadvantages of Hourly Pay
Hourly pay may not always be predictable. During slow business periods and economic downturns, employers may reduce hours instead of firing salaried staff, directly impacting earnings.
Hourly employees also tend to have less schedule flexibility. Unlike salaried workers, hourly employees must clock in on time in order to be paid and may not get any paid time off or sick leave, depending on employer policies.
Difference Between Salary vs. Hourly Pay
Salaried employees earn a fixed wage with consistent paychecks and usually receive benefits like health insurance and paid leave, but they are not eligible for overtime and may work longer hours.
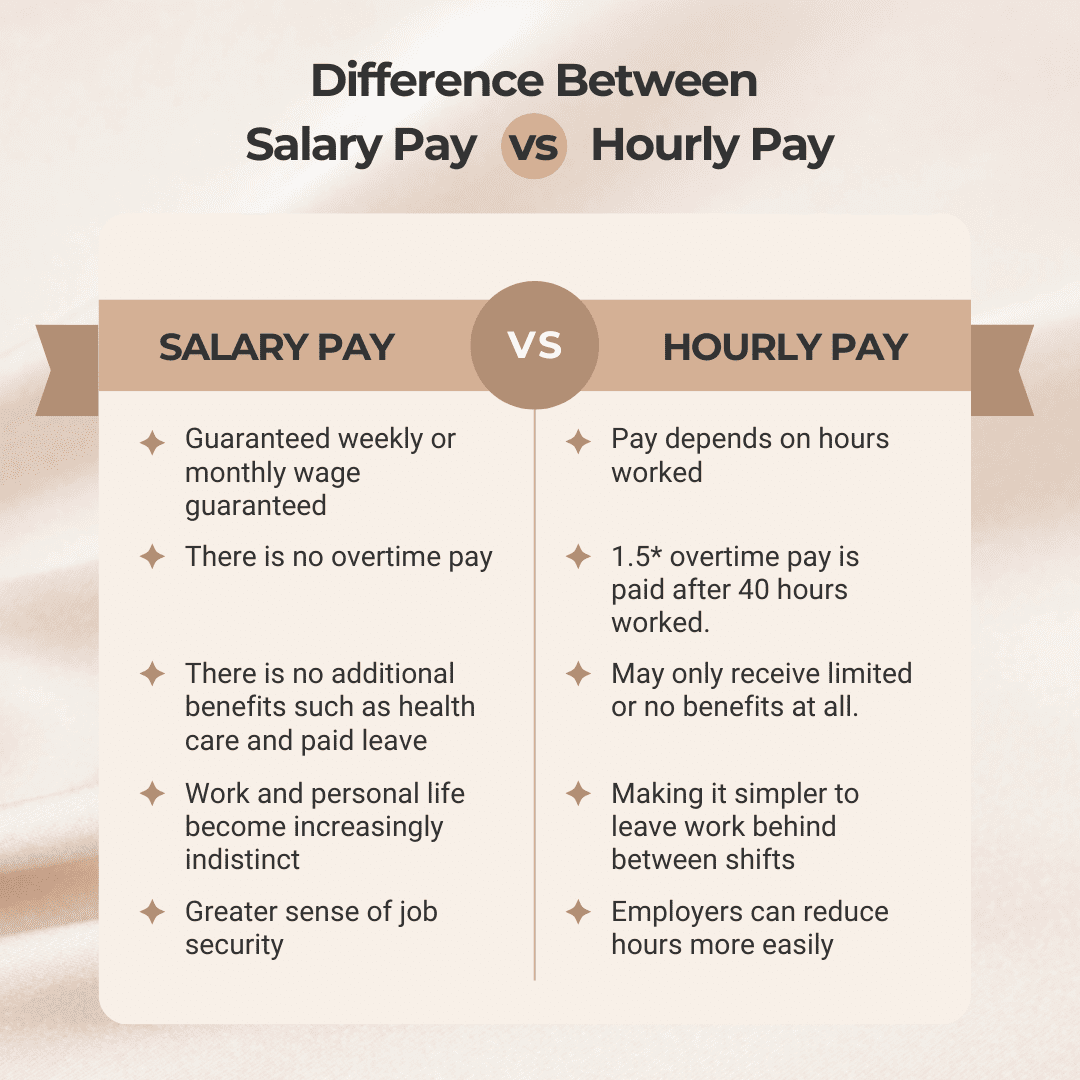
Salary pay and hourly pay differ mainly in how employees earn income, receive benefits, and manage work hours.
| Salary Pay | Hourly Pay |
|---|---|
| Guaranteed weekly or monthly wage | Pay depends on hours worked |
| No overtime pay | 1.5× overtime pay after 40 hours worked |
| Employer-provided benefits like healthcare and paid leave | May receive limited or no benefits |
| Work and personal life often overlap | Easier to leave work behind between shifts |
| Greater sense of job security | Employers can reduce hours more easily |
Role Of Paystub Generator Free For Counting Pay
Are You a Salaried or an Hourly Employee? Whatever it is, you need to count and print on your paystub with the accurate calculation. Accurate records of earnings are vital when working. Salaried employees receive a fixed paycheck regardless of hours worked; hourly employees get paid according to clocking in/clocking out.
A paystub generator free tool, can make this process much simpler by quickly creating accurate pay records in just minutes. These tools enable both employees and employers to calculate gross pay, taxes, deductions, and net pay automatically; hourly workers can monitor how overtime affects earnings, while salaried employees can ensure their fixed salary aligns with employment contracts.
FAQs:
-
Which is better, hourly rate or salary?
What kind of overtime or benefits you require will depend on your job role, whether it’s salary or Hourly, income stability needs and preferences for overtime work or benefits.
-
What is the difference between wage and salary?
Wage refers to hourly pay based on hours worked; salary refers to an annual payment.
-
What is 38 hourly to salary?
With an hourly wage rate of $38 an hour, this annual salary would amount to an impressive $79,040 annual paycheque.
-
Is it better to be an hourly or salary employee?
Your decision depends on your priorities; hourly employees typically earn overtime pay while salaried workers often enjoy consistent and generous pay and benefits packages.
-
What is 40 hourly to salary?
At a $40 hourly rate, this means your annual salary would total $83,200 per year.
-
Is it better to be salaried or hourly?
No option is universally superior; selecting one depends on factors like flexibility, overtime eligibility and benefits.
-
What is the definition of hourly pay?
Hourly pay refers to employees being paid a set sum per hour of work performed.
-
What is 31 hourly to salary?
Given an hourly wage rate of $31, the annual salary would equal $64,480.
-
What does salary mean in a job?
Salary refers to an amount that is consistently paid regardless of hours worked.
-
What is 37 hourly to salary?
At an hourly rate of $37, an annual salary would amount to $76,960.
-
Which is better, hourly rate or salary?
Ultimately, which option best meets your career security, work/life balance requirements, and income needs is up to you.
-
What is 15 hourly to salary?
Consider an hourly wage rate of $15; multiply this number by 40 hours over 52 weeks for an annual salary of $31,200.
-
Is it better to be paid hourly or salary?
Hourly pay offers the potential to generate overtime income while salary pay provides more reliable sources of revenue.
-
What are the disadvantages of salary pay?
Salaried employees may work additional hours without receiving overtime pay.
-
What is 23 hourly to salary?
Under an hourly wage rate of $23, the annual salary would be: 23 * 40* 52 = 47840 per year.
-
What are the disadvantages of being paid a salary?
Being paid a salary can erode work-life balance due to extra hours worked that may go uncompensated.
-
What is 17 hourly to salary?
Under an hourly rate of $17, an annual salary would equal $35,360 per year.
-
What is the difference between hourly pay and salary pay?
Hourly pay is determined by how many hours have been worked, while salary pay is a fixed amount.
-
Is it harder to fire a salary employee?
Salaried employees generally benefit from greater job security and protections.
-
What is 45 hourly to salary?
With an hourly wage of $45 an hour, this annualized salary would total $93,600.
-
What are the disadvantages of being paid a salary instead of an hourly rate?
Salaried employees may experience lower overtime earnings compared to hourly workers.
-
What is 29 hourly to salary?
At an hourly rate of $29, the annual salary would come out to $60,320 annually.
-
What are the cons of hourly pay?
Hourly pay can become unpredictable if work hours are reduced.
-
What is 36 hourly to salary?
With an hourly wage rate of $36 and 40-hour work weeks per year, an annual salary is $74,880.
-
What is an advantage of hourly wages?
Hourly wages offer several advantages, including eligibility for overtime pay.
-
What is 21 hourly to salary?
With an hourly wage rate of $21, the annual salary would equal $43,680.
-
What is 50 hourly to salary?
With an hourly wage rate of $50, an employee would make $104,000 annually.
-
What is 16 hourly to salary?
With a $16 hourly rate, the annual salary would equal $33,280.
-
What is 33 hourly to salary?
With an hourly wage rate of $33, the annual salary equals $68,640 per year.
-
What is 55 hourly to salary?
With an hourly wage rate of $55, this translates into an annual salary of $55 times 40 x 52 = $114,400 per year.